
Dehydration: Etiology
Background:
Hypovolemia is synonymous with extracellular fluid (ECF) volume deficit and occurs with abnormal loss of body fluid, inadequate intake, or fluid shift from plasma to interstitial space. And while dehydration shares similar etiologies, it is not synonymous with the term fluid volume deficit (hypovolemia).
Causes:
-
increase in insensible water loss or perspiration (high fever, heatstroke, etc)
-
diabetes insipidus, which is typically accompanied by polyuria
-
osmotic diuresis, which can result in polyuria caused by excess solute, such as glucose, in the renal tubules
-
hemorrhage*
-
GI losses: vomiting, NG suction, diarrhea, fistual drainage
-
overuse of diuretics
-
third-space fluid shifts: burns, intestinal obstruction
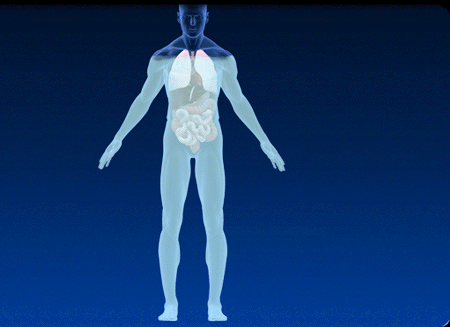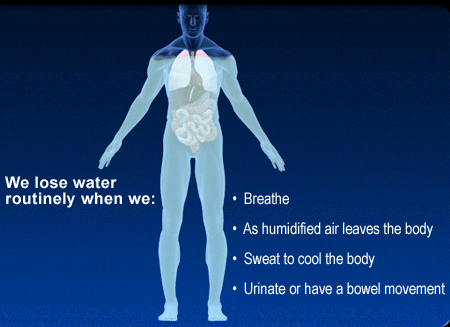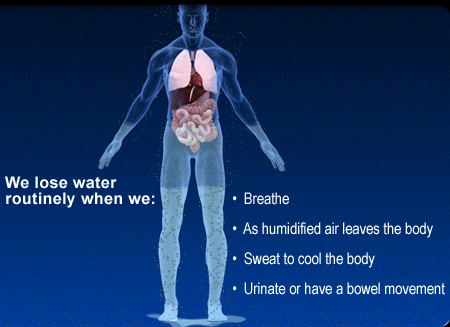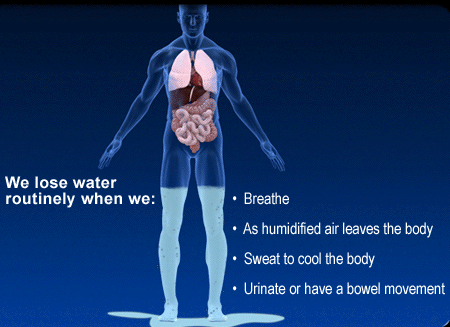
* a greater concern with hypovolemia than dehydration